Migraine headaches: understanding the causes and alleviating them with massages
Did you know that Vincent van Gogh probably suffered from migraines? In his letters, he describes flashes of light and visual disturbances - symptoms that are now considered typical of migraines with aura. A slight throbbing in the temple, a dull pressure behind the eyes - this is often how an ordinary headache begins. But migraines are different. Instead of passing, an intense, pulsating pain sets in that can last for hours or even days. This is accompanied by symptoms such as sensitivity to light and sound, nausea and visual disturbances. Millions of people worldwide are affected, but the causes are not fully understood. Sufferers know: A migraine attack can completely paralyze everyday life....
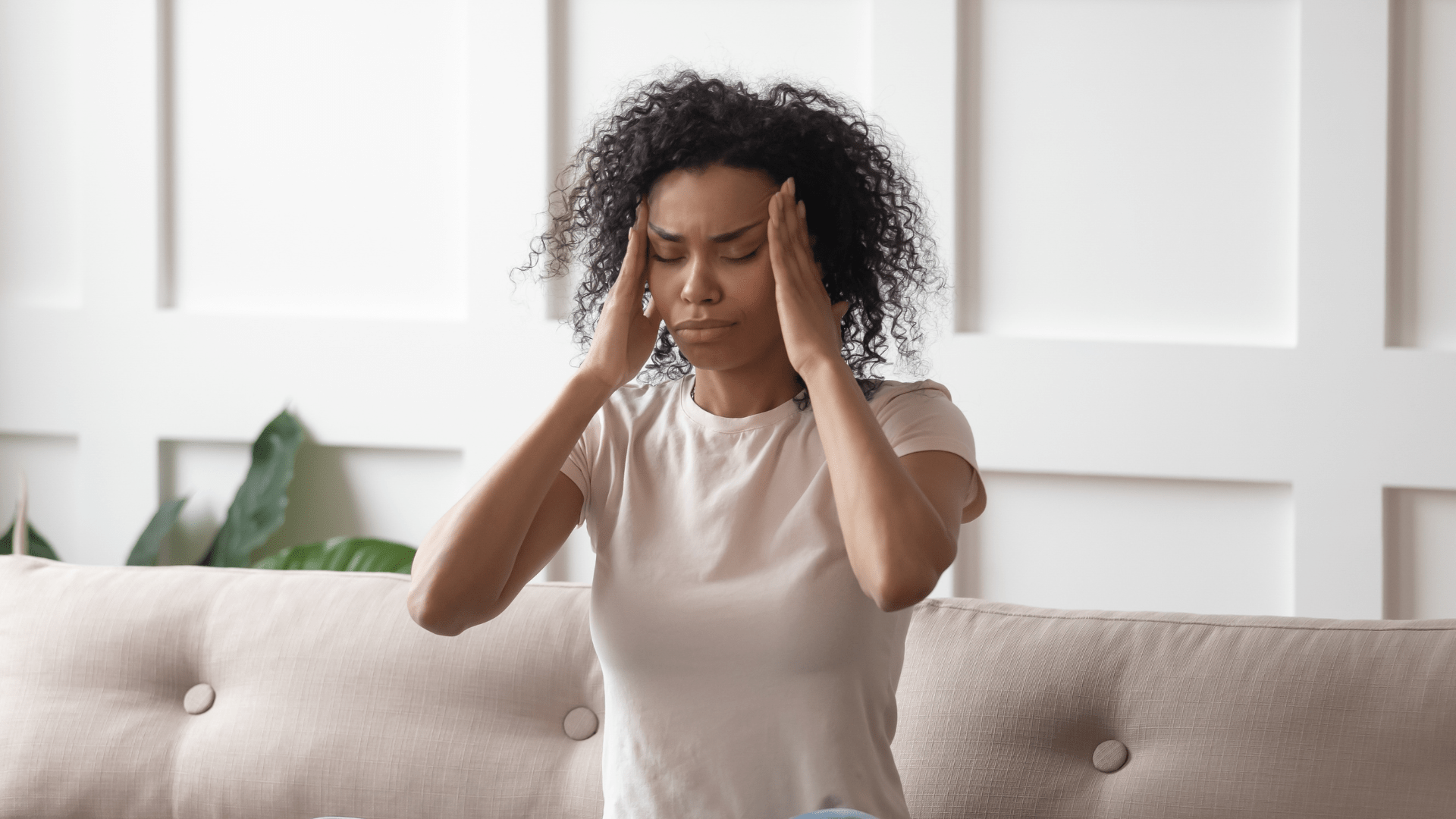


Did you know that Vincent van Gogh probably suffered from migraines? In his letters, he describes flashes of light and visual disturbances - symptoms that are now considered typical of migraines with aura.
A slight throbbing in the temple, a dull pressure behind the eyes - this is often how a normal headache begins. But migraines are different. Instead of passing, an intense, pulsating pain sets in that can last for hours or even days. This is accompanied by symptoms such as sensitivity to light and sound, nausea and visual disturbances. Millions of people worldwide are affected, but the causes are not fully understood.
Sufferers know: A migraine attack can completely paralyze your everyday life. What is behind this neurological disorder, how does it differ from normal headaches and are massages for migraines a means of relief?
Reading tipDiscover, how massages from head to toe can help with a wide range of complaints - find out more now!
What is a migraine?
Migraine is a neurological disorder that is accompanied by recurring, often severe headaches. It affects the entire nervous system and can occur with a variety of accompanying symptoms. Migraines go far beyond "classic" headaches.
Migraine vs. normal headaches - what's the difference?
Many people confuse migraines with conventional headaches. While tension headaches usually occur on both sides and manifest as a dull pressure, migraines are often one-sided and pulsating. The pain often worsens with movement and sufferers are sensitive to light and noise.
What types of migraine are there?
Not all migraines are the same. Depending on the severity, intensity and accompanying symptoms, doctors distinguish between different forms of this condition:
-
Migraine without auraMigraine without aura : occurs suddenly and without any signs.
-
Migraine with auraMigraine with aura: announces itself through neurological symptoms such as flickering, speech disorders or tingling.
-
Chronic migraine: more than 15 migraine days per month.
-
Vestibular migraineassociated with dizziness, balance disorders and nausea.
It is helpful for sufferers to know their own migraine type - because this determines which treatment options work best.
Causes and triggers - Why do migraines occur?
Although the exact causes of migraines are not yet fully understood, there are some known factors that can promote attacks. Overexcitable nerve cell activity in the brain is considered the main cause. This can be "triggered" by certain stimuli and then sets off a chain reaction that ultimately leads to the typical migraine.
What factors can trigger a migraine attack?

Not every migraine is caused by the same stimuli. Common triggers are
-
Stress and emotional tensionMigraine attacks often occur during the transition from tension to relaxation.
-
DietCertain foods such as chocolate, mature cheese, alcohol or caffeinated drinks can trigger attacks.
-
Weather changesSome migraine patients also react sensitively to particularly abrupt changes in temperature or air pressure.
-
Hormonal fluctuationsMany women experience migraine attacks in connection with their menstrual cycle or hormonal changes.
-
Lack or excess of sleep: An irregular sleep rhythm can promote migraines.
-
TensionPeople who sit a lot and are under stress are often prone to muscle tension - a factor that can intensify or even trigger migraine attacks.
Symptoms and course - How do migraines manifest themselves?
Migraine attacks typically occur in several phases. An attack usually lasts a few hours, but can also last for several days. The symptoms are quite varied.
Typical symptoms of migraine:
-
One-sided, pulsating headache - usually in the forehead, temples or eye area.
-
Sensitivity to light and noise
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Concentration problems and exhaustion
Migraine with aura vs. migraine without aura
Not every migraine attack announces itself, but around a third of sufferers experience neurological symptoms known as an aura beforehand. These include flickering or flashes of light in the field of vision, tingling or numbness and even speech disorders or dizziness.
After about 20 to 60 minutes, the headache usually sets in. However, those who do not experience an aura often only realize that an attack is imminent when the first pain occurs.
How long does a migraine attack last?
A migraine attack can last between 4 and 72 hours sometimes even longer. The duration and intensity vary greatly from person to person.
Treatment options - What helps with migraines?
Depending on the severity and frequency of the attacks, some sufferers can achieve relief with simple measures. For more intense attacks, a combination of medicinal and non-medicinal methods can be used.
What medication is available to treat migraines?
- Painkillers: For mild to moderate attacks, over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen or paracetamol can help.
- Triptans: These drugs, specially developed for migraines, constrict the dilated blood vessels in the brain and can slow down the attack.
- Antiemetics: If severe nausea occurs, drugs such as metoclopramide or domperidone are often used as a supplement.
Note: As migraine is a neurological disorder, you should always discuss the use of medication with a doctor.
Which non-medicinal forms of treatment are useful for migraines?

Of course, there are also complementary methods to reduce the frequency and intensity of migraine attacks. These have proved particularly effective:
-
Relaxation techniques: Progressive muscle relaxation, meditation or breathing exercises help to minimize stress as a trigger.
-
Exercise: Regular, moderate exercise can have a preventative effect - intensive physical exertion during an attack, on the other hand, is counterproductive.
-
Change your diet: Avoiding individual trigger foods can help reduce migraine attacks.
-
Cold or heat applications: Cold packs or warm compresses on the forehead or neck can provide relief, depending on how you feel.
Tip: You can find out more about massages and their effect on chronic pain in our article "Chronic pain and massage".
Massages against migraines - mode of action & techniques
Migraines are often associated with tension in the neck, shoulder and head area. It is therefore obvious that gentle massages can help to relieve this muscle tension. They promote blood circulation and thus reduce possible triggers. They have a calming effect on the nervous system, reduce stress levels and promote relaxation - an important aspect of migraine prevention.
Which massage techniques are particularly effective?
-
Neck and shoulder massage: Gentle kneading and stroking can relieve tension that promotes migraines.
-
Acupressure: Targeted pressure on certain points - e.g. between the eyebrows or on the temples - can alleviate pain.
-
Scalp massage: A gentle massage of the scalp promotes blood circulation and relaxes the muscles.
Initial scientific studies indicate that massages can be a promising supportive measure against migraines. A controlled study investigated the effect of classic massage and lymphatic drainage for migraine prophylaxis. The results showed that both forms of therapy led to a reduction in migraine attacks
Reading tip: You can find out more about the positive effect of massages on the psyche in our article "The effect of massages on the nervous system".
Massage chair as targeted support against migraines
As tension in the neck and shoulder area is one of the most common factors in migraines, massages are a great method of relief. Gentle massage techniques combined with the application of heat can promote blood circulation and ease muscle tension. Many models offer special programs for the head and neck area, which help to relax the entire body.
A massage chair offers an uncomplicated way to consciously take time out in everyday life and reduce inner tension.
Reading tip: Is a massage chair worth investing in your health? Find out more in our article "Is a massage chair worth it?".
Prevention - What helps to prevent migraines?
Migraines cannot be cured, but they can be significantly influenced. If you know your personal triggers and take targeted countermeasures, you can reduce the frequency and intensity of attacks. These measures have proven particularly effective in prevention:
-
Reduce stress - e.g. through meditation, yoga or mindfulness
-
Sufficient sleep - Neither too much nor too little
-
Exercise - Regular moderate activity
-
Recognize individual triggers - e.g. keep a migraine and food diary
-
Prevent tension - through targeted massages or physiotherapeutic exercises
Clear your head - how to get migraines under control
Van Gogh probably didn't have his migraine under control. You can do better! Although migraines are a complex neurological condition, a lot can be achieved with the right self-care.
Massages against migraines provide additional support: they loosen muscles, promote blood circulation and provide soothing relaxation - whether through manual applications or a massage chair. Take time for yourself regularly and you will notice how the frequency and intensity of your migraines can improve.
Cover image: fizkes, other images: Rido, Idil Demir

Co-founder and Managing Director of Massage Chair World. With his expert knowledge and industry expertise, he helps private individuals and companies to find the right massage chairs for relaxation, health and vitality. The individual expert advice is provided both by telephone or video chat, as well as in the exhibition outside Stuttgart.